Configuration
The .pages.yml file
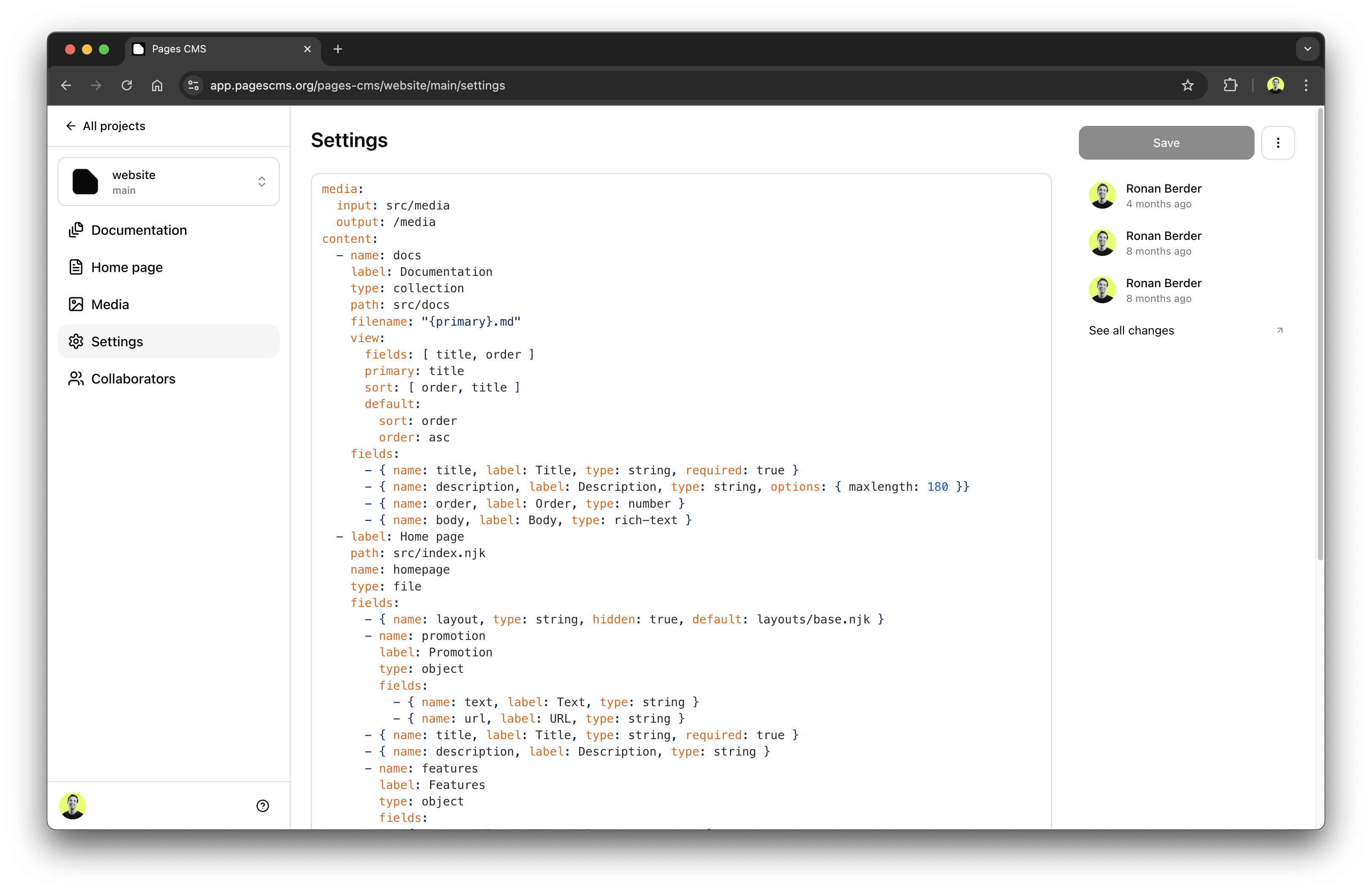
To configure Pages CMS you just need to add a .pages.yml file to the repository (and branch) that hosts your content and media. If this file isn't there when you open your repository/branch in Pages CMS, you will be presented with a link to add one via the Pages CMS interface.
You can have different configuration files on separate branches. The Pages CMS interface allows you to navigate between them (click on the name of repository at the top of the sidebar and then select the branch in the dropdown menu).
The .pages.yml file contains mainly 3 sections:
- media: the settings for media (images, videos, etc). See the "Media" section below.
- content: an array defining the content types. See the "Content" section below.
- components: an object defining reusable groups of fields. See the "Components" section below.
Media
With media, you can configure how to handle files you want to upload, attach to or embed in your content. media can be a string, a single object or an array of objects depending on whether you want a single or multiple media folders and configurations.
Keys
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Required if media is an array. Must be unique across the media array. Machine name for the media entry. |
label |
string |
Display name for the media. This will be displayed in the main menu. |
input |
string |
The path to the media folder relative to the root of the repo (e.g. src/files/media). This path is what allows us to find the files in Pages CMS to manage content and media. |
output |
string |
The path to the media folder relative to the root of the website (e.g. files/media). This path will prefix all media saved in our content, which will be used by your static site generator. |
path |
string |
The default path to present the user (e.g. when opening the media browser on an Image Field). |
extensions |
array |
An array of file extensions (strings) that should be displayed (e.g., [png, jpg]). If provided, any file with an extension not included in this list will not be shown to the user. |
categories |
array |
An array of category names (strings) to allow specific file types: image (jpg, jpeg, png, gif, svg, bmp, tif, tiff), document (pdf, doc, docx, ppt, pptx, vxls, xlsx, txt, rtf), video (mp4, avi, mov, wmv, flv), audio (mp3, wav, aac, ogg, flac) and compressed (zip, rar, 7z, tar, gz, tgz). If both extensions and categories are provided, categories might be combined or extensions might take precedence depending on the field. |
If media is set to a string, it is equivalent to settings both media.input and media.output to that value, prefixed with / for media.output.
For example, media: files/media would be equivalent to:
media:
input: files/media
output: /files/media
If we want to define multiple media configurations, we can use an array (see examples below).
Examples
Let's assume the content for my website is at the root of my repo:
media: files/media
Now, if the content for this website was in a src/ subfolder, it could look like this:
media:
input: src/media
output: media
Let's assume now that I'm hosting my website in a subfolder (e.g. hosted at http://example.com/my-website/), I may want to do the following:
media:
input: src/media
output: /my-website/media
Now, if I want to use a files/documents folder only for document uploads (e.g. pdf, doc, ppt) and another images folder with my photos that must be in .png or .webp formats, we could do the following:
media:
- name: files
label: Files
input: files/documents
output: /files/documents
categories: [ document ]
- name: images # Note: 'name' key is required here
label: Images
input: images
output: /images
extensions: [ png, webp ]
Content
Content managed by the users: collections (e.g. blog posts) and file types (e.g. the home page). The content key should be set as an array of content entries.
Keys
Each content entry can define the following keys:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Required and must be unique across the content array. Machine name for the content entry. |
label |
string |
Display name for the collection or single file. This will be displayed in the main menu. |
type |
string |
Required. collection or file, depending on whether the content entry is a collection of files with an identical schema (e.g. blog posts) or a single file (e.g. home page). |
path |
string |
Required. Path to the folder where the files are stored if it's a collection (e.g. path: src/posts, otherwise the path to the single file (e.g. path: src/index.md). |
fields |
string |
The list of fields defining the schema of the content entry (e.g. title, date, author, body, etc). See the "Fields" section below. |
filename |
string |
The pattern to generate the filename when creating a new file. This also defines how files are looked up. You can use the value of any field (e.g. ) including nested values (e.g. ). You can also use a few date tokens ({year}, {month}, {day}) and time ({hour}, {minute}, {second}) and {primary} for the primary field as defined in the view key. By default this is set to '{year}-{month}-{day}-{primary}.md'. |
exclude |
array |
An array of files to exclude from the collection (e.g. [ README.md ]). This is only valid for collections. |
view |
object |
Only valid for collections. This object defines the various options for the collection view; visible fields, sorting options and defaults, fields indexed for the search... See the "View" section below. |
format |
string |
The format of the file, used to set up the editor to edit the content: yaml-frontmatter, json-frontmatter, toml-frontmatter, yaml, json, toml, datagrid, code or raw. It defaults to yaml-frontmatter. |
subfolders |
boolean |
Whether or not the collection should display subfolders. Default to true. Set to false if you want to force the collection of files to be "flat". |
Examples
Let's assume we have a simple collection of blog posts all saved in the src/_posts folder:
content:
- name: posts
label: Posts
path: src/_posts
type: collection
fields:
# ... fields defined here ...
- name: authors
label: Authors
path: src/_data/authors.json
type: file
fields:
# ... fields defined here ...
View
The view object is only valid for type: collection content entries. It defines the configuration for the collection view, aka the page that lists the entries for a collection which is accessed from the main menu under a specific repo/branch (e.g. https://app.pagescms.org/pages-cms/template-nextjs/content/posts/).
Keys
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
fields |
array |
List of the fields to be displayed in the collection view (e.g. fields: [ title, published, author ]). This can include nested fields and values (e.g. fields: [ title, published, "tags[0]", author.name ]). If not defined, it defaults to just the primary field (see below). The order of the fields is kept in the collection view. |
primary |
string |
The name of the field that should be used as the primary field (e.g. primary: title). If undefined, it will be set to the title field if it exists, otherwise the first field define in the content entry (e.g. content.posts.fields[0].name). |
sort |
array |
The list of fields that the collection can be sorted by (e.g. sort: [ date, title ]). By default, it is set to the date (if any) and the primary field. |
search |
array |
The list of fields that should be indexed for search. By default, all fields are indexed. |
default |
object |
Define the default values for search and sorting: { search: 'My keywords', sort: title, order: asc }). default.order can be asc or desc. By default, default.search is empty, default.sort is the first field in the sort array and default.order is set to desc. |
layout |
string |
Controls the visual layout of the collection view, either list (default) or tree for a collapsible tree view. |
node |
string or object |
If a string, it will be treated as the value for node.filename. If an object, it can have 2 attributes: filename for the filename of the nodes (e.g. index.md) and hideDirs (can be all, nodes or others to hide either all folders, only node folders or folders other than the nodes'). A node is typically a nested file in a subfolder (e.g. folder/subfolder/index.md) that will show up as if it were in its parent folder (e.g. folder/) and act as the parent of all of its siblings in the subfolder. It is useful either if entries in your collection are nested (e.g. 2025-01-01-my-post/index.md) or if you want to show a tree layout with nodes as parents of the subfolders' entries. |
Examples
Assuming you have a date field and title is the primary field, your default configuration would look like:
view:
fields: [ title ]
primary: title
sort: [ date, title ]
default:
search: ''
sort: title
order: desc
This would display the title of each post and sort them by title in descendant order (start with special characters and numbers, all the way to z).
Let's assume we also have the following:
published, a boolean that defines whether or not the post is published,author, a string set to the name of the author.
Let's set the view to only display the posts from Patricia, display title, date and the published state with the newer posts first:
view:
fields: [ title, date, published ] # title is the first entry and thus will be set to primary
sort: [ date, title, published ]
default:
search: 'author:Patricia'
sort: date
order: desc
The author:Patricia syntax comes from lunr.js, the search library used by Pages CMS under the hood. Other syntax will work too (wildcards, boosts, fuzzy matches and term presence).
If I wanted to show a tree view of my collection, with some nodes:
view:
layout: tree
node:
filename: index.md
hideDirs: all # This will hide all subfolders, even if they do not contain a node
Components
Components allow you to define reusable groups of fields or field configurations. They act like templates that can be referenced within your content entries.
Components are defined under a top-level components key in your .pages.yml file. This key holds an object where each key is a unique component name, and the value is the component definition. A component definition follows the same structure as a standard Field definition but without the name key.
Component Definition Keys
The keys used to define a component are the same as those used for Fields, except the name key (which is defined by the key in the components object).
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
label |
string |
Display name for the component. Primarily used for documentation or if referenced directly in certain UI contexts. |
type |
string |
The underlying base type of the component (e.g., object, text, image). Often object when grouping fields. If undefined but fields is present, defaults to object. |
fields |
array |
If type is object, this lists the fields contained within this component. These follow the standard Field definition structure. |
component |
string |
Allows a component to inherit from another component. The value should be the name (key) of the component to inherit from. Properties from the inheriting component will override the base component. |
| ... | ... | Other standard field keys like description, default, list, hidden, required, pattern, options can be used to configure the component itself. |
Examples
Here's an example defining two components: a hero component with a headline and cover image, and a simple email component defining a reusable string field with pattern validation.
components:
hero: # 'hero' is the component name/key
label: Hero Section
type: object
fields:
- name: headline
label: Headline
type: text
required: true
- name: cover
label: Cover Image
type: image
email: # 'email' is the component name/key
label: Email Address
type: string
pattern:
regex: '^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$'
message: 'This must be a valid email address (e.g. [email protected]).'
These components can then be referenced by their name using the component key within the fields definition of your content types or even within other components.
Fields
Fields define the structure and data types for your content entries or components.
Keys
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Required (unless defining a component directly under the components key) and must be unique within its parent fields array. Machine name for the field. body is reserved for the main content of the file when dealing with a frontmatter format (e.g., YAML frontmatter). |
label |
string |
Display name for the field. This is what is displayed in the edit form. If omitted, the name is used. |
description |
string |
Help text displayed below the field in the form. |
type |
string |
Defines the type of field. Can be a single type name: block, boolean, code, date, file, image, number, object, reference, rich-text, select, string, text or uuid. If undefined, it defaults to text unless fields is defined (then it defaults to object). |
component |
string |
Allows a field to inherit its properties (like type, label, nested fields, options, etc.) from a defined Component. The value should be the name (key) of the component to inherit from. Properties defined directly on the field (like name, label, required) will override those inherited from the component. The type inherited from the component takes precedence over any type defined on the field itself. |
default |
(any) | Default value for the field when a new entry is created. |
list |
boolean or object |
If truthy, the field is an array of values (of the type defined for the field). See the "List" section below. |
hidden |
boolean |
If true, the field will not be displayed in the form but will be saved. It is usually used with default to set a required field that shouldn't be edited by users, like for example the language of a post (lang: en-US). |
required |
boolean |
If true, the field can't be empty. |
pattern |
string or object |
A regular expression to validate the field. A custom message for the error can be provided by defining an object with regex and message attributes (e.g. pattern: { message: 'This must be a valid email address (e.g. [email protected]).', regex: '^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$' }) |
fields |
array |
Only valid for object fields. List of the fields in that object. |
options |
object |
Options for that field. Refer to the field specific details below. |
List
Any field with a truthy list key will be stored as an array of that field type. For example:
- name: images
label: Images
type: image
list: true
Will allow the user to save multiple image paths:
images:
- media/image-1.png
- media/image-2.png
list can be an object with min, max, default and collapsible keys. min and max define the minimum and maximum number of entries in the array. For example:
- name: tags
label: Tags
type: string
list:
min: 1 # Must have at least one tag
max: 5 # Can have up to five tags
default: [news] # Default value when creating new entry
This will force the user to enter at least 1 tag and at most 5.
By default, list entries are collapsible. You can disable this behavior by setting collapsible to false:
- name: tags
label: Tags
type: string
list:
collapsible: false
You can also configure the collapsible behavior by setting collapsible to an object with collapsed and summary properties:
- name: sections
label: Sections
type: object
list:
collapsible:
collapsed: true # Default collapsed state
summary: "{title} ({index})" # Template string using field values and {index}
The summary template string can use:
- Field values using
{fields.fieldName}syntax - The index of the item using
{index}
Certain fields (e.g. the image field) implement their own list logic for handling multiple elements with the mutliple option. You can use either one approach, both result in an array of values.
Field Types
- Block field
- Boolean field
- Code field
- Date field
- File field
- Image field
- Number field
- Object field
- Reference field
- Rich-text field
- Select field
- String field
- Text field
- UUID field
Settings
This allows you to apply global settings within this repository and branch.
Keys
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
hide |
boolean |
If set to true, the "Settings" link/page will be hidden in the Pages CMS UI. |
content |
object |
An object containing settings specifically related to content handling. |
content |
object |
An object containing settings specifically related to content handling. |
content.merge |
object |
Defaults to false. If set to true, when saving an existing content entry, the submitted fields will be merged with the fields already present in the file. Fields present only in the file will be preserved. Fields present in both will take the value from the submitted form. If false, the file content will be completely overwritten with the submitted form data (after processing according to the schema). This is helpful if you want to expose only parts of your file for editing. |
Examples
To hide the settings editor and enable the content merge behavior:
settings:
hide: true
content:
merge: true
To just enable the content merge behavior:
settings:
content:
merge: true